Abstract
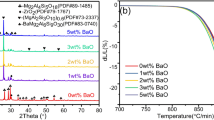
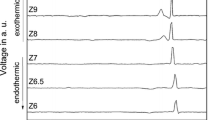
Formation of machinable glass–ceramic in the system MgO–SiO2–Al2O3–K2O–B2O3–F with and without addition of MgF2 has been investigated. Crystallization of glass sample was done by controlled thermal heat treatment at nucleation and crystallization temperatures. The results showed that MgF2 in high concentration had a synergistic effect and enhanced the formation of interlocked mica crystals. Non-isothermal DTA experiments showed that the crystallization activation energies of base glasses were changed in the range of 235–405 kJ/mol, while the crystallization activation energies of samples with addition of MgF2 were changed in the range of 548–752 kJ/mol.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Hameed S A M, Ghoniem N A, Saad E A and Margha F H 2005 Ceram. Int. 31 499
Arora A, Shaaban E R, Singh K and Pandey O P 2008 J. Non-Cryst. Solids 355 23
Baik D S, No K S, Chun J S and Cho H Y 1997 J. Mater. Proc. Technol. 67 50
Boccaccini A R 1997 J. Mater. Proc. Technol. 65 302
Greene K, Pomeroy M J, Hampshire S and Hill R 2003 J. Non-Cryst. Solids 325 193
Kissinger H E 1957 Anal. Chem. 29 1702
Likitvanichkul S and Lacourse W C 1995 J. Mater. Sci. 30 6151
Matusita K and Sakka S 1980 J. Non-Cryst. Solids 38/39 741
Ozawa T 1971 Polymer 12 150
Radonjic Lj and Nikolic Lj 1991 J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 7 11
Riello P, Canto P, Comelato N, Polizzi S, Verita M and Hopfe S 2001 J. Non-Cryst. Solids 288 127
Taruta S, Mukoyama K, Suzuki S S, Kitajima K and Takusayawa N 2001 J. Non-Cryst. Solids 296 201
Wang P, Yu L, Xiao H, Cheng Y and Lian S 2009 Ceram. Int. 35 2633
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
GHASEMZADEH, M., NEMATI, A. Role of MgF2 on properties of glass–ceramics. Bull Mater Sci 35, 853–858 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-012-0379-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-012-0379-2